/ Interface / Audio Settings
Menubar . Workspace Panel . Log Panel
Audio Monitor Panel . Audio Settings
Code Editor . Image Editor
SoundEditor . SoundPlayer . EnvelopeEditor
Plugin Explorer Dialog . Sample Manager Dialog
Wherein we empower you to tinker with your audio engine configurations.
THe Audio Settings Dialog controls the initialization options for the underlying OS-specific audio devices. It is found in the settings menu via
Audio Settings....Note:
- you can inspect all devices known to Hz via
Probe Audio Settings...menu button. Results of the probe are displayed in the Log Panel.- you can establish initial audio settings via Hz command-line options
Audio Settings Dialog
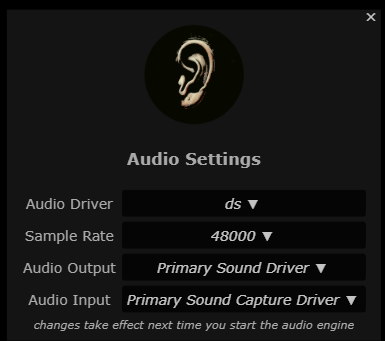
Audio API
Some operating systems support multiple Audio APIs for access to the devices connected to you computer. Mac users are usually not subject to this confusion because its core audio API is sufficiently high-performance and configurable as to preclude the need for alternatives.
Sadly, on Windows and Linux, this isn't the case.
Windows users commonly select one of ASIO, DS (Direct Sound) or WASAPI
while on Linux, typical options are ALSA, Pulse, or JACK.
Conceptually the APIs deliver different performance characteristics while "driving" all audio devices on your computer. It's possible, however, that each API will "see" a different set of devices and this constraint may factor into your selection decision.
If you don't know which driver to choose, try each one, running one or more of the examples between selections. As stated in the dialog, the settings are applied when the audio engine is started, so if you want to try a different API you must stop the current audio session, then restart it.
Sample Rate
Each combination of API and device supports a set of sample rates with a default of either 44100 Hz, or 48000 Hz. Other rates may be available on a device and will incur performance vs quality tradeoffs. If you are unsure, we suggest you select 48000 Hz.
Audio Output
Most computers have at least two optional output devices: headphones and
speakers. If you select default, then the OS-default will be applied.
This means that changes via OS-specific sound settings will affect
the setting in Hz. There are cases where you might like to
decouple your OS sound (to eg listen to podcasts) from the device that
you route Hz output to. This is often useful in recording sessions
to monitor the input signal without feedback.
Audio Input
Most computers have a least one optional input device: the microphone. If you have a webcam or Audio Interface, you may see guitar, external microphone, etc. here. No matter, the choice you make here follows the same rules as with Audio Output. Note that in order to process the input signal, your scripts must refer to it via the MusicAPI ADC anode. Two channel audio interfaces often allow you to wire in a guitar and a microphone and you can use a channel-splitter anode to route each signal to a different chain.