Ref / Hz.Plugins / Hz.Syntho
Hz.Filt, Hz.Echo, Hz.Delay, Hz.Reverb
Hz.Mix, Hz.LFO, Hz.ADSR
see also Hz.Builtins, Plugin Explorer, Hz.Plugins Examples
Wherein we present Hz.Syntho- a curiously configurable synthesizer.
Right-click to navigate sections.
Intro
Hz.Syntho is a configurable, polyphonic synthesizer.
Each voice sports up to 3 oscillators, 4 lfos,
2 filters, 2 envelopes and 3 mixers.
These can be dynamically routed in a modular style. A shared reverb unit
can also be enabled to round out the final sound. Additional global effects
can be added by routing the output of Hz.Syntho to your favorite
effects plugin(s).
Hz.Syntho comes with several presets so you can explore its
possibiities quickly. The oscillators support custom wavetables
and so the sounds you can produce are virtually unlimited.
WebGUI
At the top of an Hz.Sytho panel are 4 controls:
download: syncs parameters from host
upload: sends parameters to host
bookmark: param presets menu
schema: graph presets menu
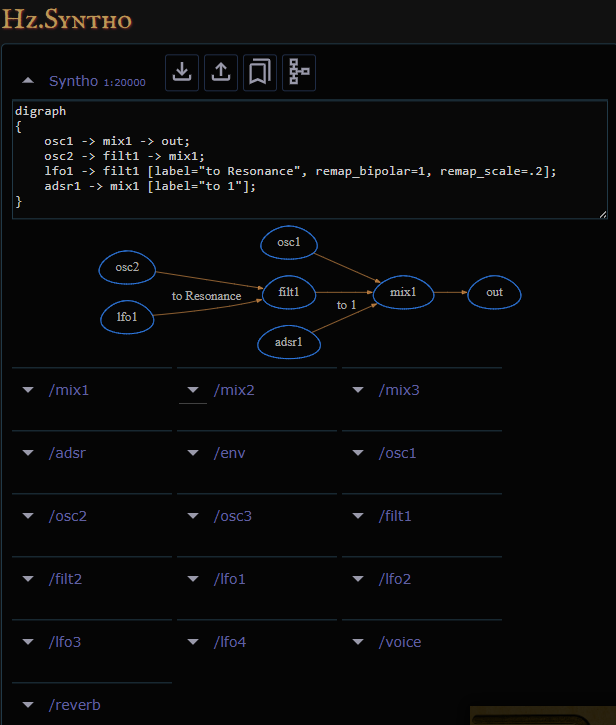
Modular Routing with Dot Notation
Signal routing in Hz.Syntho is configured symbolically using
dot notation
and the resulting network can be visualized in the WebGUI as seed below.
digraph
{
osc1 -> mix1 -> out;
osc2 -> filt1 -> mix1;
lfo1 -> filt1 [label="to Resonance", remap_bipolar=1, remap_scale=.2];
adsr1 -> mix1 [label="to 1"];
}
As seen above, default signal routing is trivial, just
issue statements of the form srcnode -> sinknode ... ;,
where the available nodes are:
| Node | Description | Count |
|---|---|---|
mix# |
Hz.Mix | 1-3 |
osc# |
Hz.Osc | 1-3 |
filt# |
Hz.Filt | 1-2 |
lfo# |
Hz.LFO | 1-4 |
adsr |
Hz.ADSR | 1 |
env |
Hz.ADSR | 1 |
out |
to Syntho global effects (eg Hz.Reverb) | 1 |
NB: reverb can't be referred to in the digraph since it is applied to
the combined polyphonic output. You can, however, refer to its
parameters as desribed below.
You can route the output of a node to
a parameter or side-chain audio port by providing the label attribute
on the sink node as shown above with to Resonance and to 1.
Finally, when routing to a parameter you can remap the upstream
output by including one or more remap values:
| Name | Description | Range (dflt) |
|---|---|---|
remap_mute |
Disables the remapping | 0 or 1 (0) |
remap_bipolar |
converts the signal range from 0-1 to -.5-.5 | 0 or 1 (0) |
remap_scale |
scales the signal) | >0 (1) |
remap_power |
remaps the signal through a power curve | -5-5 (0) |
remap_offset |
adds an offset to the signal | -100-100 (0) |
Parameters
Since Syntho plays the role of orchestrating the interplay between
modules, all parameters reside within each module's namespace. The
exception to the rule are the preset parameters described next.
Module parameter names are found for each module and you can
fully-qualify their names for syntho.SetParam() by prepending
the module name like so: /mix1/Gain.
Here are links to the parameter tables for Syntho's modules:
mix, osc, adsr, env, lfo, filt, reverb
NB: ignore submodule parameters within some of these pages as they are
superceded by the Samplo's modules.
Presets
| Syntho Preset Params | Description |
|---|---|
_dotgraph |
A string containing the node-graph in dot notation with newlines escaped. |
_worklist |
A string containing the compiled node-graph. You can produce this from the dotgraph via Agraph.SynthoWorklist(dotgraph, synthoInstance) |
Note that Syntho always operates from a worklist and until you provide
it with one, it will use the builtin or initial value. To support the
live updates to the dotgraph, the GUI periodically updates Syntho
with a new worklist. If you don't use the GUI, here's how to produce
one. Note that this requires
const wl = Agraph.SynthoWorklist(yourdot, syntho);
await syntho.LoadPreset({_worklist: wl});
In addition to these special preset parameters, normal module parameters can
also be initialized via the Syntho.constructor preset or its LoadPreset
method.
Here's a snippet from one of the examples:
const _dotgraph = `digraph
{
lfo1 -> osc2 [label="to Transpose", remap_scale=10];
osc2 -> osc1 -> mix1 -> out;
adsr1 -> mix1 [label="to 1"];
}`;
let randomChoice = 5; // lfo.Style is an enum
let syntho = scene.NewAnode("Hz.Syntho", {
name:"Syntho",
preset:
{
_dotgraph: _dotgraph.replace(/\n/g, "\\n"), // escape newlines
"mix1": {
Gain: -6 // dB
},
"adsr": {
A: .2,
R: .2,
S: .5,
T: 0,
},
"osc1": {
Amplitude: .4,
Waveform: 0, // 0: sine, 1 is square,
UnisonVoices: 3,
UnisonDetune: 5, // semitones
UnisonSpread: .5,
PMScale: 8,
UnisonVoices: 3,
},
"osc2" : {
Amplitude: 6, // PM amount
},
"lfo1": {
// choices are [0-1] for plotting, mod-remapping applied in graph
// choices are wired to transpose which is measured in semitones.
_choices: [0, .3, .7, .9],
Style: randomChoice,
Period: .1, // seconds (2hz)
Loop: 1
},
"reverb": {
Model: 1 ,
Wet: .9 ,
SSRoomSize: 30,
}
}});