Ref / Hz.Plugins / Hz.Samplo
Hz.Filt, Hz.Echo, Hz.Delay, Hz.Reverb
Hz.Mix, Hz.LFO, Hz.ADSR
see also Hz.Builtins, Plugin Explorer, Hz.Plugins Examples
Wherein we explore Hz.Samplo, a player of audio sample files.
Right-click to navigate sections.
Intro, SynthModes
Hz.Samplo is a polyphonic player of audio sample files. Like most synthesizers,
it responds to Anode Note and MIDI events.
Audio sample files for Hz.Samplo come in three categories according to the
associated mode of sound synthesis. You must select the SynthMode upon anode
creation.
// create an instance and select Wavetable synthesis (SynthMode:1).
let samplo = scene.NewAnode("Hz.samplo", {preset:{SynthMode: 1}});
Soundfont Player
A soundfont player maps each MIDI-note to one or more sound files. The mapping can be sensitive to velocity (or other note expression). Soundfonts can be stereo or mono. They can also be sparse and result in resampled and/or interpolated sample file evaluation.
As a soundfont player, Hz.Samplo is comparable to
FluidSynth but where FluidSynth employs
a single, large .sf2 file Hz.Samplo plays individual .mp3, .wav and
.flac files. The SampleMgr API and
Sample Manager Dialog can help you
browse and preload groups of sample files into Hz.Samplo. You can
even create your own sound fonts composed of your own sounds.
Wavetable Synthesizer
A wavetable synthesizer employs a single monophonic audio sample file.
A wavetable contains one or more variations of a canonical waveform. A
variation is selected explicitly via a Wavetable Index parameter but
this is often driven by an LFO or program change. The wtlfo GUI subpanel
groups parameters controlling the builtin LFO that can be used to drive
Wavetable Index.
Hz.Samplo supports two wavetable formats. .wav files are used by synths like
Serum and include one
or more monophonic variations comprising 4096 samples. There is no
conventional file extension for .wav files that conform to this
structure so you'll need to verify conformance by other means.
.vitaltable files are used by Vital Synth and
are explicit in their wavetable identity. Both Hz.Syntho and
Hz.Osc support wavetable synthesis and these two wavetable
representations.
Granular Synthesizer
A granular synthesizer employs a (usually larger, sometimes randomly selected)
audio sample file and synthesizes sound by performing small snippets of the file,
called grains, in a structured manner. Granular synthesis can be thought of
as a generalization of wavetable synthesis where the canonical sound and its
variations are controlled dynamically with a larger collection of parameters.
The large parameter space can be daunting but also quite powerful. Hz.Samplo
includes a collection of parameters than control its granular synthesis
engine. Note that you can use a single audio sample file or use the
soundfonts managed by SampleMgr as discussed above.
Webview GUI
At the top of an Hz.Samplo panel are 3 buttons controlling groups of parameters:
download: syncs parameters from host
upload: sends parameters to host
bookmark: presets menu
The GUI configures itself according to the SynthMode.
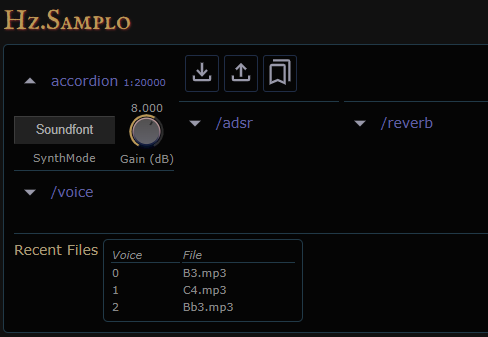
Soundfont Mode
Here is the GUI when operation in Soundfont mode. Note that an
additional Pan parameter will only appear if the current soundfont
is monophonic. Also note that additional controls are found within
/adsr, /reverb, and /voice subpanels. The Recent Files region
displays a snapshot of the sound files in use by each polyphonic
voice.
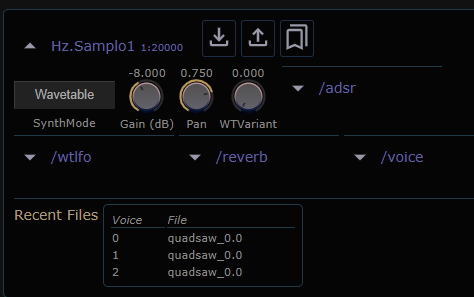
Wavetable Mode
Here's the GUI when operating in Wavetable mode. Note that Pan,
WTVariant, and the /wtlfo subpanel appear in this mode.
As mentioned above, you can use wtlfo to drive the WTVariant
parameter. You can find out more about the builtin lfo here.
Also note that Recent Files shows which wavetable variant is in
used by each voice. The portion of the filename following _ encodes
both wavetable index and the fractional value between two adjacent
wavetables employed.
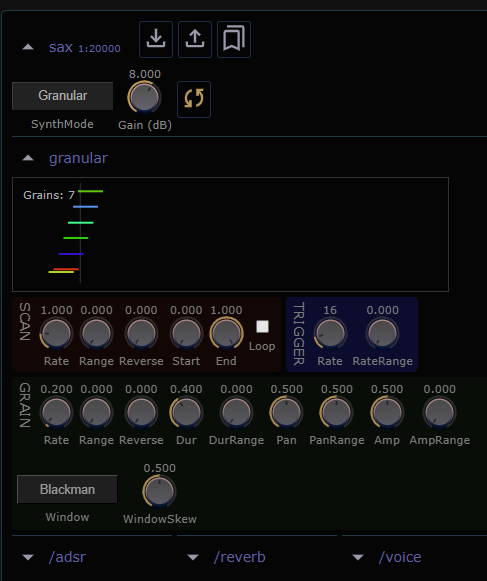
Granular Mode
Here's the GUI when operating in Granular mode. Note that
a new subpanel, /granular appears. In addition to its three
parameter groupings, SCAN, TRIGGER and GRAIN you can also
see a grain visualization region that shows the current
scan position as well as small rectangles representing the
active grains for the first polyphonic voice. The vertical
position of a grain represents its completion stages. New
grains appear at the top. Completed grains are at the bottom.
The left-to-right axis conveys the position withing the soundfile
as well as each grain duration. For high scan rates and depending upon
the power of your computer, the Grains display can get bogged down.
If this happens you can disable the update via the
autorenew toggle button at top.
Parameters
| Name | Id | Description | Range (dflt) |
|---|---|---|---|
SynthMode |
100 | Selects the mode of sythesis. Must be set during anode creation. | 0:Soundfont, 1:Wavetable, 2:Granular (0) |
Gain |
101 | Controls the overall output gain expressed in decibels (db). | -40-40 (0) |
Pan |
102 | Selects the Pan for monophonic sample files only. | 0 - 1 (.5) |
Wavetable Parameters
| Name | Id | Description | Range (dflt) |
|---|---|---|---|
WavetableVariant |
111 | If the current wavetable has variants, this selects one expressed in pct of the total. This parameter may be modulated by /wtlfo or an external modulator. |
0-1 (0) |
Granular Parameters
| Name | Id | Description | Range (dflt) |
|---|---|---|---|
GrScanRate |
121 | Multiplier for rate to scan the current sample file. | 0-5 (1) |
GrScanRateRange |
122 | The amount to randomize the scan rate | 0-1 (0) |
GrScanReversePct |
123 | The likelihood that a scan we be reversed. | 0-1 (0) |
GrScanStart |
124 | The start position within the current sample file representing the starting point. Represented as a pct of the file length. | 0-1 (0) |
GrScanEnd |
125 | The end position for the scanner. Must be greater than the start position. | 0-1 (1) |
GrScanLoop |
126 | Scanning ends when NoteOff is received. If the scanner reaches the end of a scan prior to that, Loop controls whether to jump back the the start and keep scanning. |
0 or 1 (0) |
GrTriggerRate |
127 | The rate, in grains per second, that new grains are created. Higher values result in more live grains and a higher system load. | 0-100 (10) |
GrTriggerRateRange |
128 | Nonzero values randomize the trigger rate resulting in non-aligned grains. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainRate |
129 | The relative rate to play each grain. | 0-5 (1) |
GrainRateRange |
130 | A randomizer for grain rate. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainReversePct |
131 | The probablity that a grain will play reversed. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainDur |
132 | Duration of a grain in seconds | 0-1 (.1) |
GrainDurRange |
133 | A randomizer for grain duration. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainPan |
134 | The pan position for a grain. | 0-1 (.5) |
GrainPanRange |
135 | A randomizer for each grain's pan position. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainAmp |
136 | Scales each grain's amplitude. More live grains produce more sound. Works in conjunction with the Gain parameter. |
0-1 (.5) |
GrainAmpRange |
137 | A randomizer for each grain's amplitude. | 0-1 (0) |
GrainWindow |
139 | An amplitude envelope for each grain. | 0:None, 1:Sine, 2:Hann, 3:Hamming, 4:Blackman, 5:Bartlett, 6:PlanckTaper85, 7:PlanckTaper95 (4) |
GrainWindowSkew |
139 | Skews the GrainWindow toward the front (0) or back (1). A value of 0 produces a more "plucky" attack. |
0-1 (.5) |
GrUpdateGUI |
140 | Controls whether the Grains display is updated. Turn this off when the GUI is bogged down by large grain counts. | 0 or 1 (1) |
Preset
Samplo is configured with a _maxGrains preset value which limits
the number of live grains per voice in Granular Synth mode. The default
value of 100 can be overridden but this must be done during node-creation
using the preset mechanism as shown here:
let samplo = scene.NewAnode("Hz.samplo", {preset:{SynthMode: 2, _maxGrains:200}});